| Active Ingredient | RUXOLITINIB PHOSPHATE |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAKAFI | (NDA) 202192 | INCYTE CORP | TABLET;ORAL | EQ 5MG BASE, EQ 10MG BASE, EQ 15MG BASE, EQ 20MG BASE, EQ 25MG BASE | EQ 5MG BASE, EQ 10MG BASE, EQ 15MG BASE, EQ 20MG BASE, EQ 25MG BASE (RS) | November 16, 2011 | - | November 16, 2018, December 4, 2021 | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug O Orphan drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
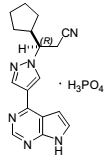 |
| Chemical Name | (R)-3-(4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-3-cyclopentylpropanenitrile phosphate |
| CAS No | 941678-49-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18N6 |
| Molecular Weight | 404.36 |
| Appearance | a white to off-white to light pink powder |
| Solubility | It is soluble in aqueous buffers across a pH range of 1 to 8. |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in aqueous buffers across a pH of 1-8 |
| Polymorphism | Polymorphism has been shown to exist for ruxolitinib phosphate drug substance and only one anhydrous crystalline form has been used. Anhydrous crystalline form used is the most stable solid form. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 13.89 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 5.51 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 2.94 (Predicted) |
| Identification | IR, X-ray |
| Degradation | Photostability data was also provided. One batch was directly exposed to light (1200 and 2400klux). Exposure of the free base to light (1200 and 2400klux) causes a change in the colour of the active substance and showed that the free base is sensitive to light. Therefore it is recommended that ruxolitinib phosphate should be protected from light where possible. |
| Hygroscopic | - |
| Photostability study | Photo sensitive |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | I |
| Manufacture of API | Ruxolitinib phosphate is chemically synthesised inseven steps. Adequate in-process controls are applied during the synthesis. The specifications and control methods for intermediate products, starting materials and reagents, have been presented. The active substance is purified by recrystallisation. Batch analysis data produced with the proposed synthetic route provided show that the active substance can be manufactured reproducibly. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | Jakafi is indicated for treatment of patients with intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, including primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis and post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis. Jakafi is indicated for treatment of patients with polycythemia vera who have had an inadequate response to or are intolerant of hydroxyurea. |
| Dosage and Administration | In Myelofibrosis, the recommended starting dose of Jakafi is based on platelet count (Refer FDA Label). A complete blood count (CBC) and platelet count must be performed before initiating therapy, every 2 to 4 weeks until doses are stabilized, and then as clinically indicated. Doses may be titrated based on safety and efficacy. |
| Mechanism of action | Ruxolitinib, a kinase inhibitor, inhibits Janus Associated Kinases (JAKs) JAK1 and JAK2 which mediate the signaling of a number of cytokines and growth factors that are important for hematopoiesis and immune function. JAK signaling involves recruitment of STATs (signal transducers and activators of transcription) to cytokine receptors, activation and subsequent localization of STATs to the nucleus leading to modulation of gene expression. Myelofibrosis (MF) and polycythemia vera (PV) are myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) known to be associated with dysregulated JAK1 and JAK2 signaling. In a mouse model of JAK2V617F-positive MPN, oral administration of ruxolitinib prevented splenomegaly, preferentially decreased JAK2V617F mutant cells in the spleen and decreased circulating inflammatory cytokines (eg, TNF-α, IL-6). |
| Absorption | In clinical studies, ruxolitinib is rapidly absorbed after oral Jakafi administration with maximal plasma concentration (C max ) achieved within 1 to 2 hours post-dose. Based on a mass balance study in humans, oral absorption of ruxolitinib was estimated to be at least 95%. Mean ruxolitinib Cmax and total exposure (AUC) increased proportionally over a single dose range of 5 to 200 mg. |
| Food Effect | There were no clinically relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of ruxolitinib upon administration of Jakafi with a high-fat meal, with the mean C max moderately decreased (24%) and the mean AUC nearly unchanged (4% increase). |
| Distribution | The mean volume of distribution at steady-state is 72 L in patients with MF with an associated inter-subject variability of 29% and 75 L in patients with PV with an associated inter-subject variability of 23%. Binding to plasma proteins in vitro is approximately 97%, mostly to albumin. |
| Metabolism | In vitro studies suggest that ruxolitinib is metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9. |
| Elimination | Following a single oral dose of [14C]-labeled ruxolitinib in healthy adult subjects, elimination was predominately through metabolism with 74% of radioactivity excreted in urine and 22% excretion via feces. Unchanged drug accounted for less than 1% of the excreted total radioactivity. The mean elimination half-life of ruxolitinib is approximately 3 hours and the mean half-life of ruxolitinib + metabolites is approximately 5.8 hours. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 1 to 2 hours |
| Half life | 5.8 hours |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender | In healthy subjects, no significant differences in ruxolitinib pharmacokinetics were observed with regard to gender and race. In a population pharmacokinetic evaluation in patients with MF, no relationship was apparent between oral clearance and patient age or race, and in women, clearance was 17.7 L/h and in men, 22.1 L/h with 39% inter-subject variability. Clearance was 12.7 L/h in patients with PV, with a 42% inter-subject variability, and no relationship was apparent between oral clearance and gender, patient age or race in this patient population. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29480 | A | II | May 29, 2015 | CHONGQING HUAPONT PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| Parameters | Details | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 5MG | 10MG | 15MG | 20MG | 25MG | |
| Excipients used | microcrystalline cellulose (68.35MG), lactose monohydrate (71.45MG), magnesium stearate (0.80MG), colloidal silicon dioxide (1.60MG), sodium starch glycolate (4.80MG), povidone (3.20MG) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (3.20MG) | microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, povidone and hydroxypropyl cellulose | microcrystalline cellulose (205.05MG), lactose monohydrate (214.35MG), magnesium stearate (2.40MG), colloidal silicon dioxide (4.80MG), sodium starch glycolate (14.40MG), povidone (9.60MG) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (9.60MG) | microcrystalline cellulose (273.40MG), lactose monohydrate (285.80MG), magnesium stearate (3.20MG), colloidal silicon dioxide (6.40MG), sodium starch glycolate (19.20MG), povidone (12.80MG) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (12.80MG) | microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, povidone and hydroxypropyl cellulose | |
| Composition of coating material | - | |||||
| Composition of caspule shell | - | |||||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
The properties of the active substance suggested that a tablet manufacturing process based upon wet granulation might be suitable for development of a market formulation. The excipients selected are standard ingredients intablet formulations, and are in compliance with internationally accepted pharmacopoeial standards. During the development the influence of the medium pH and the dissolution behaviour of the tablets were investigated. The results showed that dissolution medium pH has no significant impact on the dissolution due to the high solubility of the substance over the physiological pH range. Dissolution method developed was shown to be discriminatory however not optimal for the higher strength. Therefore unless other dissolution methods are shown to be non-discriminatory, the proposed dissolution method should be replaced. It is recommended to develop and replace the propose method with a more optimal one. The composition is: lactose monohydrate (filler), cellulose microcrystalline (filler), sodium starch glycolate (disintegrant), magnesium stearate (lubricant), stearic acid (lubricant), colloidal silicon dioxide (Glidant), hydroxypropyl cellulose (binder), povidone (binder). |
|||||
| Manufacture of the product | - | |||||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |
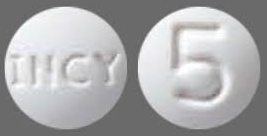
|
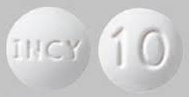
|

|

|
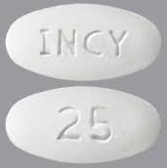
|
|
| Appearance | round and white, debossed with “INCY” on one side and “5” on the other | round and white, debossed with “INCY” on one side and “10” on the other | oval and white, debossed with “INCY” on one side and “15” on the other | capsule-shaped and white, debossed with “INCY” on one side and “20” on the other | oval and white, debossed with “INCY” on one side and “25” on the other | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with “INCY” on one side and “5” on the other | Debossed with “INCY” on one side and “10” on the other | Debossed with “INCY” on one side and “15” on the other | Debossed with “INCY” on one side and “20” on the other | Debossed with “INCY” on one side and “25” on the other | |
| Score | no score | no score | no score | no score | no score | |
| Color | WHITE | WHITE | WHITE | WHITE | WHITE | |
| Shape | ROUND | ROUND | OVAL | CAPSULE | OVAL | |
| Dimension | 7mm | 9mm | 15mm | 16mm | 18mm | |
| Mfg by | Novartis Pharma (EU) | |||||
| Mfg for | Incyte Corporation (US) | |||||
| Marketed by | Incyte Corporation (US), Novartis Pharma (EU) | |||||
| Distributed by | - | |||||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N202192 | 1 | 7598257 | December 24, 2027 | Y | Y | U - 1201 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 7598257 | December 24, 2027 | Y | Y | U - 1201 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 8415362 | December 24, 2027 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 8722693 | June 12, 2028 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 8822481 | June 12, 2028 | - | - | U - 1573 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 8829013 | June 12, 2028 | - | - | U - 1201 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 8829013 | June 12, 2028 | - | - | U - 1201 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 9079912 | December 12, 2026 | - | - | U - 1721 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 9079912 | December 12, 2026 | - | - | U - 1721 | - | Download |
| N202192 | 1 | 9662335 | December 12, 2026 | DS | - | - | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | 0.1 N HCI | 900 | 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 | June 25, 2015 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | JAKAVI | Download |
| UK | JAKAVI | Download |
| US | JAKAFI | Download |
| Exclusivity Code: Exclusivity Expiration is I - 699: Dec 4, 2017. |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
